The Data Cloud remains one of Salesforce’s most enigmatic products, often touted for its seemingly ‘magical’ capabilities. Recently, Salesforce made waves by announcing complimentary Data Cloud licenses (albeit with certain restrictions), prompting numerous organizations to explore this platform’s potential. Salesforce Data Cloud Terminology.
When diving into any significant facet of the Salesforce ecosystem, navigating a learning curve is par for the course. Familiarizing oneself with the terminology and its practical implications is a crucial starting point to feeling confident with the technology.
Introducing Your Guide to Salesforce Safety Net 3
Within this guide, we explain essential terminology to grasp data modeling concepts and elucidate how data traverses through various stages within the Data Cloud, culminating in the activation of refined segments.
- Primary Key vs. Foreign Key
Understanding these foundational concepts in data sourcing is pivotal when working with the Data Cloud. Given the diverse origins of streamed data, akin to Marketing Cloud data extensions, a grasp of these terms proves invaluable.
Primary Key: A distinguishing field within a dataset, such as the Salesforce record ID. Foreign Key: Facilitates linking data across distinct tables or sources; for instance, correlating an OrderID between customer records and order details datasets from an eCommerce platform.
- Data Ingestion
To satiate the voracious appetite of the Data Cloud, ingestion serves as the conduit for feeding it with data. Various methods, including SDKs, Connectors, and the Ingestion API, facilitate this process.
SDKs: Accelerate integration setup, with examples like the Interactions SDK and Engagement Mobile SDK from Salesforce. Connectors: Pre-built integrations simplifying connections between Salesforce products and Data Cloud. Ingestion API: Enables developers to construct integrations from scratch for data sources not covered by SDKs or connectors.
- Data Streams
Datasets from disparate sources enter the Data Cloud as data streams, with their frequency of updates dictated by operational needs and API capabilities.
Real-time data streams: Immediate data updates. Batched data streams: Data updates occur at predetermined intervals, such as hourly or daily.
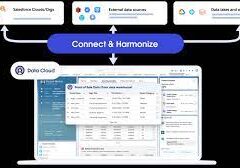
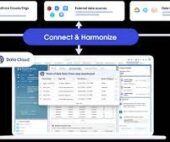
- Data Source Object, Data Lake Object, and Data Model Object
Visualize the Salesforce data model, where objects relate to one another; these objects collaboratively manage ingested data within the Data Cloud.
Data Source object: Initial repository for ingested data in its raw format. Data Lake object: Facilitates data mapping to other sources and applies transformations. Data Model object: Resembles Salesforce objects structurally, facilitating relational data management without storing data internally.
- Data Mapping (Mapping Canvas)
The mapping canvas provides a visual interface for aligning disparate data points, crucial for rendering ingested data usable through mappings from data source to data lake objects.
During this process, primary keys and match/reconciliation rules are specified.
- Identity Resolution
Data Cloud’s strength lies in resolving discrepancies to compile comprehensive records, essential for maintaining unified profiles across platforms without merging records.
- Match Rules
Building upon traditional Salesforce duplicate and matching rules, Data Cloud offers deterministic and probabilistic matching, catering to various data representation nuances.
- Reconciliation Rules
Similar to Salesforce deduplication concepts, reconciliation rules determine the preferred value for fields, aiding in mass deduplication.
- Source Priority
Ranking data sources according to reliability helps prioritize trustworthy data over less accurate sources within the Data Cloud.
- Unified Profile
Identity resolution culminates in unified profiles, representing the ‘golden record’ of individuals, adaptable to evolving data streams.
- Calculated Insights
Comparable to Salesforce roll-up fields, calculated insights derive new data points from existing ones, enriching data analysis capabilities.
- Streaming Insights
Streaming insights offer real-time or near-real-time analysis, suited for smaller datasets requiring swift insights.
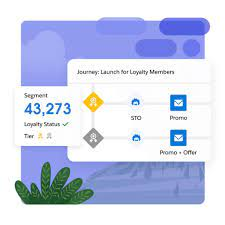
- Activation Target
Activation transpires when perfected segments are dispatched to destinations for personalized interactions, spanning Marketing Cloud, advertising platforms, and other repositories.
- Data Action
Data actions trigger alerts or events based on streaming insights and engagement data, fostering automation and integration across Salesforce platforms.
In Summary
Mastering the Data Cloud entails navigating its terminologies and understanding how data evolves through its lifecycle, culminating in the activation of refined segments for personalized interactions.