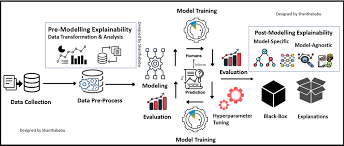
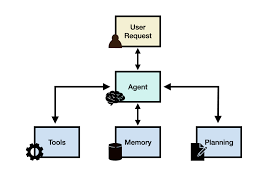
What is Explainable AI
Building a trusted AI system starts with ensuring transparency in how decisions are made. Explainable AI is vital not only for addressing trust issues within organizations but also for navigating regulatory challenges. According to research from Forrester, many business leaders express concerns over AI, particularly generative AI, which surged in popularity following the 2022 release