The AI Capability Maturity Model (AI CMM), devised by the Artificial Intelligence Center of Excellence within the GSA IT Modernization Centers of Excellence (CoE), functions as a standardized framework for federal agencies to evaluate their organizational and operational maturity levels. It is equally useful for private organizations in aligning them with predefined objectives. Instead of imposing normative capability assessments, the AI CMM concentrates on illuminating significant milestones indicative of maturity levels along the AI journey.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!The AI Capability Maturity Model focuses primarily on the development of AI capabilities within an organization. It evaluates an organization’s maturity across four main areas: data, algorithms, technology, and people.
Serving as a valuable tool, the AI CMM assists organizations in shaping their unique AI roadmap and investment strategy. The outcomes derived from AI CMM analysis empower decision-makers to identify investment areas that address immediate goals for rapid AI adoption while aligning with broader enterprise objectives in the long run.
Maturity vs capability models
A maturity model tends to measure activities, such as whether a certain tool or process has been implemented. In contrast, capability models are outcome-based, which means you need to use measurements of key outcomes to confirm that changes result in improvements.
AI development rooted in sound software practices underpins much of the content discussed in this and other chapters. Though not explicitly delving into agile development methodology, Dev(Sec)Ops, or cloud and infrastructure strategies, these elements are fundamental to the successful development of AI solutions. The AI CMM elaborates on how a robust IT infrastructure leads to the most successful development of an organization’s AI practice.
What are the maturity levels of AI?
What are the maturity levels of Artificial Intelligence?
- Level 1: Technology Awareness.
- Level 2: Experimental activation of AI.
- Level 3: The operationalization of AI to innovate processes or products.
- Level 4: A systems approach and the creation of new business models.
- Level 5: The Future of Artificial Intelligence.
Or it can be measured this way.
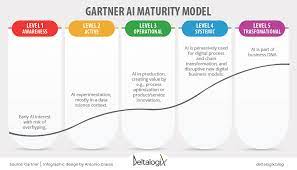
AI Maturity Model
- Level 1. Awareness.
- Level 2. Active.
- Level 3. Operational.
- Level 4. Systemic.
- Level 5. Transformational.
- Explore current business practices.
- Brainstorm new decisions that make your company more valuable.
- AI adoption case study.
Why is AI maturity important?
The AI Maturity Assessment is a process designed to help organizations evaluate their current AI capabilities, identify gaps and areas for improvement, and develop a roadmap to build a more effective AI program.
Organizational Maturity Areas
Organizational maturity areas represent the capacity to embed AI capabilities across the organization. Two approaches, top-down and user-centric, offer distinct perspectives on organizational maturity.
Top-Down, Organizational View
- Initial / Ad Hoc: Process is unpredictable, poorly controlled, and unmanaged.
- Repeatable: Process is documented and steps are repeatable with consistent results, often reactionary.
- Defined: Documented, standardized processes that improve over time.
- Managed: Activities are effectively measured, and meeting objectives are based on active management and evidence-based outcomes.
- Optimized: Continuous performance improvement through incremental and innovative improvements.
Bottom-Up, User-centric View
- Individual: No organizational team structure around activities. Self-organized and executed.
- Team Project: A dedicated, functional team organized around process activities. Organized by skill set or mission.
- Program: Group of related projects managed in a coordinated way. Introduction of structured program management.
- Portfolio: Collection of projects, programs, and other operations that achieve strategic objectives.
- Enterprise: Operational activities and resources organized around enterprise strategy and business goals.

Operational Maturity Areas
Operational maturity areas represent organizational functions impacting the implementation of AI capabilities. Each area is treated as a discrete capability for maturity evaluation, yet they generally depend on one another.
PeopleOps
- Initial / Ad Hoc Individual Project: Self-directed identification and acquisition of AI-related skillsets.
- Repeatable Team Project: Identify types of AI talent for the lifecycle; employee journey created.
- Defined Program: PeopleOps program established; conduct talent gaps analysis; talent map created; training identified.
- Managed Portfolio: PeopleOps program linked to measurable performance objectives; an optimized enterprise integrated ownership culture throughout the organization.
CloudOps
- Initial / Ad Hoc Individual Project: Minimal cloud resources or individual user account.
- Repeatable Team Project: Innovation sandbox in the cloud.
- Defined Program: Dev, test, and prod environments available but manual resource allocation.
- Managed Portfolio: Self-service or templated cloud resource allocation.
- Optimized Enterprise: Balanced cloud resource sharing across the organization with robust cost/benefit/usage metrics.
DevOps
- Initial / Ad Hoc Individual Project: Development on a local workstation.
- Repeatable Team Project: Process exists for moving locally developed tools into production, but some parts are manual.
- Defined Program: Established secure process for containerizing tools and moving into a production environment.
- Managed Portfolio: Increasingly automated process for deploying secure software with an emphasis on reducing iteration and delivery timelines.
- Optimized Enterprise: Fully managed secure software container orchestration; CI/CD/CATO.
SecOps
- Initial / Ad Hoc Individual Project: Code security/validation is manually accomplished in the test environment; container security is default to orchestration.
- Repeatable Team Project: Code security/validation is manually accomplished within the pipeline; container security is baselined at orchestration.
- Defined Program: Code/container security and validation are automated within the pipeline and manually approved.
- Managed Portfolio: Code/container security and validation software are automated and automatically approved; software rollouts are “trusted.”
- Optimized Enterprise: Pipeline security software feeds central Security Data Lake; automation embedded at the pipeline orchestration layers; automated code rollbacks; ongoing authorization.
DataOps
- Initial / Ad Hoc Individual Project: “Shoeboxes” of data stored locally, not discoverable; copied from one machine to another.
- Repeatable Team Project: Routine data sources available and well-documented, but new data discovery is ad hoc; exploratory data analysis initiated.
- Defined Program: Engineering support for data management activities is explicit; data pipeline exists.
- Managed Portfolio: Self-service for adding new data sources, preparing datasets, and curating data for ML projects.
- Optimized Enterprise: Intelligent, secure data discovery, access, and use across all organizations with metrics on business usage and compliance.
MLOps
- Initial / Ad Hoc Individual Project: Models and methods are selected ad hoc and not documented.
- Repeatable Team Project: Implement methods for documenting experiments and model selection; utilization of GPUs initiated.
- Defined Program: Model and methods catalog exist; model-to-use case matching leverages previous historical knowledge; model measures model accuracy and speed prediction.
- Managed Portfolio: Increased use of infrastructure/server-based GPU acceleration for model development; automated selection, testing, and evaluating ML models using AutoML.
- Optimized Enterprise: Use of hyperscale GPU acceleration; feedback from ML tools captured, and models are continuously updated and improved.
AIOps
- Initial / Ad Hoc Individual Project: Reactionary and ad hoc AI capability identification.
- Repeatable Team Project: Established process to capture AI product requirements and user workflows.
- Defined Program: Formal AI Product Management team, strategy, and roadmap, including a test and evaluation plan.
- Managed Portfolio: AI Product Management goals are linked to organizational performance objectives; T&E synthesis and evaluation included for each AI product.
- Optimized Enterprise: AI capability dependencies are mapped across org boundaries and linked to an enterprise strategy with measurable objectives; retrospective analysis of past efforts to continuously modify business objectives related to AI investment; dedicated T&E efforts to optimize AI capabilities.
AI Capability Maturity Model
This comprehensive overview of organizational and operational maturity areas underlines the multifaceted nature of AI implementation and the critical role played by diverse elements in ensuring success across different layers of an organization.
How AI is transforming the world?
AI-powered technologies such as natural language processing, image and audio recognition, and computer vision have revolutionized the way we interact with and consume media. With AI, we are able to process and analyze vast amounts of data quickly, making it easier to find and access the information we need.