Why Choose Fundingo for Your Salesforce Loan Management Needs?
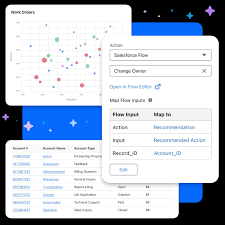
In today’s fast-evolving financial sector, businesses need solutions that boost efficiency, enhance customer experience, and streamline operations. Fundingo, a premier loan management platform, seamlessly integrates with Salesforce to deliver a powerful, all-in-one lending solution. This article explores the key advantages of Fundingo for Salesforce loan management, including automated workflows, real-time data visibility, superior CRM capabilities, and advanced reporting tools. 1. Streamlined Loan Processing with Automation Target Keywords: Integrated Loan Management Solution, Efficiency in Loan Processing Key Benefits: Traditional loan processing is often bogged down by repetitive tasks, leading to delays and inefficiencies. Fundingo’s Salesforce-native integration automates underwriting, document collection, and compliance checks—cutting processing times while improving accuracy. The result? A leaner, faster, and more scalable loan management system. 2. Real-Time Data Visibility for Smarter Decisions Target Keywords: Data Visibility in Loan Management Key Benefits: Many lenders struggle with data silos—critical borrower information trapped in disconnected systems. Fundingo eliminates this issue by integrating directly with Salesforce CRM, ensuring all loan data is updated in real time. Whether tracking delinquencies, monitoring portfolio health, or generating compliance reports, lenders gain unmatched transparency for data-driven decision-making. 3. Strengthen Customer Relationships with Salesforce CRM Target Keywords: Customer Relationship Management in Lending Key Benefits: In lending, customer experience is everything. Fundingo leverages Salesforce’s CRM tools to help lenders build stronger relationships. Automated communications, tailored loan offers, and proactive support ensure borrowers stay satisfied—leading to higher retention rates and increased referrals. 4. Advanced Reporting & Analytics for Strategic Growth Target Keywords: Reporting Tools for Loan Management Key Benefits: Without robust reporting, lenders operate blindly. Fundingo’s built-in analytics transform raw data into actionable insights, helping financial institutions mitigate risk, identify growth opportunities, and comply with regulations—all from within Salesforce. 5. The Power of Integration: Fundingo + Salesforce Target Keywords: Value Proposition of Integrated Systems Why Integration Beats Standalone Systems: ✅ Cost Savings – Eliminate redundant tools and manual processes.✅ Scalability – Grow your lending operations without switching platforms.✅ Seamless User Experience – No more juggling multiple logins or data exports. Unlike traditional Loan Origination Systems (LOS), which operate in isolation, Fundingo’s native Salesforce integration ensures a unified, future-proof solution. Industry leaders confirm: integrated lending platforms drive efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. Conclusion: Elevate Your Lending Operations with Fundingo Choosing Fundingo for Salesforce loan management means investing in speed, transparency, and customer-centric lending. By combining automation, real-time data, CRM excellence, and powerful analytics, Fundingo empowers lenders to work smarter, reduce risk, and grow faster. Ready to transform your loan management? Contact Tectonic today. Like Related Posts Salesforce OEM AppExchange Expanding its reach beyond CRM, Salesforce.com has launched a new service called AppExchange OEM Edition, aimed at non-CRM service providers. Read more The Salesforce Story In Marc Benioff’s own words How did salesforce.com grow from a start up in a rented apartment into the world’s Read more Salesforce Jigsaw Salesforce.com, a prominent figure in cloud computing, has finalized a deal to acquire Jigsaw, a wiki-style business contact database, for Read more Service Cloud with AI-Driven Intelligence Salesforce Enhances Service Cloud with AI-Driven Intelligence Engine Data science and analytics are rapidly becoming standard features in enterprise applications, Read more