Return on Sales (ROS)
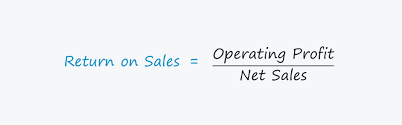
Return on Sales (ROS): Definition, Calculation & How to Improve It Want to know how efficiently your business converts sales into profit? Who doesn’t? Return on Sales (ROS) measures operational efficiency, helping you maximize earnings and identify wasteful spending. Even profitable businesses can struggle with cash flow if they overspend on marketing, R&D, or other expenses—leaving little profit despite high revenue. ROS answers: “How much profit do we keep from each dollar of sales?” Let’s break down what ROS is, how to calculate it, and strategies to improve it. What Is Return on Sales (ROS)? Return on Sales (ROS) is a profitability ratio that shows how much of your revenue turns into operating profit. Also called operating profit margin, it excludes interest and taxes, focusing purely on operational efficiency. Formula: ROS=(Operating ProfitNet Sales)×100ROS = (Net SalesOperating Profit)×100 ROS vs. ROI vs. Net Profit Margin Metric What It Measures Key Difference ROS Profit from operations (before interest & taxes) Focuses on operational efficiency ROI (Return on Investment) Profit generated from an investment Measures effectiveness of capital spent (e.g., new equipment, marketing) Net Profit Margin Profit after all expenses (taxes, interest, etc.) Shows final profitability after all costs How to Calculate ROS Step-by-Step Formula Example Calculation Item Amount Revenue $10,000,000 Returns $1,000,000 COGS $2,000,000 Operating Expenses (SG&A) $4,000,000 Operating Profit $3,000,000 Net Sales $9,000,000 ROS = (3,000,0009,000,000)×100=∗∗33.3%∗∗ROS=(9,000,0003,000,000)×100=∗∗33.3%∗∗ What Is a Good ROS? It depends on your industry. Here are average benchmarks: Industry Average ROS Healthcare 6-30%* Hotels 8-15% Manufacturing 6-8% Restaurants 3-7% Retail 2-5% Tech 10-20%+ *Higher for specialized services (e.g., surgical centers at 30%) Key Insight: If ROS declines as revenue grows, your costs may be rising too fast. 5 Ways to Improve Your ROS 1. Optimize Pricing Strategy 2. Reduce Costs 3. Boost Operational Efficiency 4. Improve Sales Process 5. Lower Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) Why ROS Matters Pro Tip: Monitor ROS quarterly—if it drops, investigate rising costs or pricing issues. Summary ROS is a powerful metric for assessing how well your business turns sales into profit. By optimizing pricing, cutting costs, and improving efficiency, you can increase profitability and ensure sustainable growth. Like Related Posts Salesforce OEM AppExchange Expanding its reach beyond CRM, Salesforce.com has launched a new service called AppExchange OEM Edition, aimed at non-CRM service providers. Read more The Salesforce Story In Marc Benioff’s own words How did salesforce.com grow from a start up in a rented apartment into the world’s Read more Salesforce Jigsaw Salesforce.com, a prominent figure in cloud computing, has finalized a deal to acquire Jigsaw, a wiki-style business contact database, for Read more Service Cloud with AI-Driven Intelligence Salesforce Enhances Service Cloud with AI-Driven Intelligence Engine Data science and analytics are rapidly becoming standard features in enterprise applications, Read more