How the Atlas Reasoning Engine Powers Agentforce
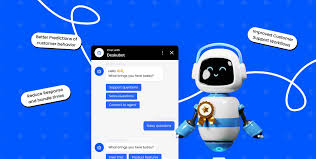
Autonomous, proactive AI agents form the core of Agentforce. But how do they operate? A closer look reveals the sophisticated mechanisms driving their functionality. The rapid pace of AI innovation—particularly in generative AI—continues unabated. With today’s technical advancements, the industry is swiftly transitioning from assistive conversational automation to role-based automation that enhances workforce capabilities. For artificial intelligence (AI) to achieve human-level performance, it must replicate what makes humans effective: agency. Humans process data, evaluate potential actions, and execute decisions. Equipping AI with similar agency demands exceptional intelligence and decision-making capabilities. Salesforce has leveraged cutting-edge developments in large language models (LLMs) and reasoning techniques to introduce Agentforce—a suite of ready-to-use AI agents designed for specialized tasks, along with tools for customization. These autonomous agents can think, reason, plan, and orchestrate with remarkable sophistication, marking a significant leap in AI automation for customer service, sales, marketing, commerce, and beyond. Agentforce: A Breakthrough in AI Reasoning Agentforce represents the first enterprise-grade conversational automation solution capable of proactive, intelligent decision-making at scale with minimal human intervention. Several key innovations enable this capability: Additional Differentiators of Agentforce Beyond the Atlas Reasoning Engine, Agentforce boasts several distinguishing features: The Future of Agentforce Though still in its early stages, Agentforce is already transforming businesses for customers like Wiley and Saks Fifth Avenue. Upcoming innovations include: The Third Wave of AI Agentforce heralds the third wave of AI, surpassing predictive AI and copilots. These agents don’t just react—they anticipate, plan, and reason autonomously, automating entire workflows while ensuring seamless human collaboration. Powered by the Atlas Reasoning Engine, they can be deployed in clicks to revolutionize any business function. The era of autonomous AI agents is here. Are you ready? Like Related Posts Salesforce OEM AppExchange Expanding its reach beyond CRM, Salesforce.com has launched a new service called AppExchange OEM Edition, aimed at non-CRM service providers. Read more The Salesforce Story In Marc Benioff’s own words How did salesforce.com grow from a start up in a rented apartment into the world’s Read more Salesforce Jigsaw Salesforce.com, a prominent figure in cloud computing, has finalized a deal to acquire Jigsaw, a wiki-style business contact database, for Read more Service Cloud with AI-Driven Intelligence Salesforce Enhances Service Cloud with AI-Driven Intelligence Engine Data science and analytics are rapidly becoming standard features in enterprise applications, Read more