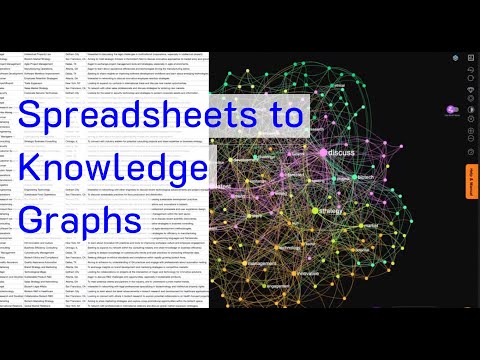
Neo4j Runway and Healthcare Knowledge Graphs Recently, Neo4j Runway was introduced as a tool to simplify the migration of relational data into graph structures. LLMs Turn CSVs into Knowledge Graphs. According to its GitHub page, “Neo4j Runway is a Python library that simplifies the process of migrating your relational data into a graph. It provides tools that abstract communication with OpenAI to run discovery on your data and generate a data model, as well as tools to generate ingestion code and load your data into a Neo4j instance.” In essence, by uploading a CSV file, the LLM identifies the nodes and relationships, automatically generating a Knowledge Graph. Knowledge Graphs in healthcare are powerful tools for organizing and analyzing complex medical data. These graphs structure information to elucidate relationships between different entities, such as diseases, treatments, patients, and healthcare providers. Applications of Knowledge Graphs in Healthcare Integration of Diverse Data Sources Knowledge graphs can integrate data from various sources such as electronic health records (EHRs), medical research papers, clinical trial results, genomic data, and patient histories. Improving Clinical Decision Support By linking symptoms, diagnoses, treatments, and outcomes, knowledge graphs can enhance clinical decision support systems (CDSS). They provide a comprehensive view of interconnected medical knowledge, potentially improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment effectiveness. Personalized Medicine Knowledge graphs enable the development of personalized treatment plans by correlating patient-specific data with broader medical knowledge. This includes understanding relationships between genetic information, disease mechanisms, and therapeutic responses, leading to more tailored healthcare interventions. Drug Discovery and Development In pharmaceutical research, knowledge graphs can accelerate drug discovery by identifying potential drug targets and understanding the biological pathways involved in diseases. Public Health and Epidemiology Knowledge graphs are useful in public health for tracking disease outbreaks, understanding epidemiological trends, and planning interventions. They integrate data from various public health databases, social media, and other sources to provide real-time insights into public health threats. Neo4j Runway Library Neo4j Runway is an open-source library created by Alex Gilmore. The GitHub repository and a blog post describe its features and capabilities. Currently, the library supports OpenAI LLM for parsing CSVs and offers the following features: The library eliminates the need to write Cypher queries manually, as the LLM handles all CSV-to-Knowledge Graph conversions. Additionally, Langchain’s GraphCypherQAChain can be used to generate Cypher queries from prompts, allowing for querying the graph without writing a single line of Cypher code. Practical Implementation in Healthcare To test Neo4j Runway in a healthcare context, a simple dataset from Kaggle (Disease Symptoms and Patient Profile Dataset) was used. This dataset includes columns such as Disease, Fever, Cough, Fatigue, Difficulty Breathing, Age, Gender, Blood Pressure, Cholesterol Level, and Outcome Variable. The goal was to provide a medical report to the LLM to get diagnostic hypotheses. Libraries and Environment Setup pythonCopy code# Install necessary packages sudo apt install python3-pydot graphviz pip install neo4j-runway # Import necessary libraries import numpy as np import pandas as pd from neo4j_runway import Discovery, GraphDataModeler, IngestionGenerator, LLM, PyIngest from IPython.display import display, Markdown, Image Load Environment Variables pythonCopy codeload_dotenv() OPENAI_API_KEY = os.getenv(‘sk-openaiapikeyhere’) NEO4J_URL = os.getenv(‘neo4j+s://your.databases.neo4j.io’) NEO4J_PASSWORD = os.getenv(‘yourneo4jpassword’) Load and Prepare Medical Data pythonCopy codedisease_df = pd.read_csv(‘/home/user/Disease_symptom.csv’) disease_df.columns = disease_df.columns.str.strip() for i in disease_df.columns: disease_df[i] = disease_df[i].astype(str) disease_df.to_csv(‘/home/user/disease_prepared.csv’, index=False) Data Description for the LLM pythonCopy codeDATA_DESCRIPTION = { ‘Disease’: ‘The name of the disease or medical condition.’, ‘Fever’: ‘Indicates whether the patient has a fever (Yes/No).’, ‘Cough’: ‘Indicates whether the patient has a cough (Yes/No).’, ‘Fatigue’: ‘Indicates whether the patient experiences fatigue (Yes/No).’, ‘Difficulty Breathing’: ‘Indicates whether the patient has difficulty breathing (Yes/No).’, ‘Age’: ‘The age of the patient in years.’, ‘Gender’: ‘The gender of the patient (Male/Female).’, ‘Blood Pressure’: ‘The blood pressure level of the patient (Normal/High).’, ‘Cholesterol Level’: ‘The cholesterol level of the patient (Normal/High).’, ‘Outcome Variable’: ‘The outcome variable indicating the result of the diagnosis or assessment for the specific disease (Positive/Negative).’ } Data Analysis and Model Creation pythonCopy codedisc = Discovery(llm=llm, user_input=DATA_DESCRIPTION, data=disease_df) disc.run() # Instantiate and create initial graph data model gdm = GraphDataModeler(llm=llm, discovery=disc) gdm.create_initial_model() gdm.current_model.visualize() Adjust Relationships pythonCopy codegdm.iterate_model(user_corrections=”’ Let’s think step by step. Please make the following updates to the data model: 1. Remove the relationships between Patient and Disease, between Patient and Symptom and between Patient and Outcome. 2. Change the Patient node into Demographics. 3. Create a relationship HAS_DEMOGRAPHICS from Disease to Demographics. 4. Create a relationship HAS_SYMPTOM from Disease to Symptom. If the Symptom value is No, remove this relationship. 5. Create a relationship HAS_LAB from Disease to HealthIndicator. 6. Create a relationship HAS_OUTCOME from Disease to Outcome. ”’) # Visualize the updated model gdm.current_model.visualize().render(‘output’, format=’png’) img = Image(‘output.png’, width=1200) display(img) Generate Cypher Code and YAML File pythonCopy code# Instantiate ingestion generator gen = IngestionGenerator(data_model=gdm.current_model, username=”neo4j”, password=’yourneo4jpasswordhere’, uri=’neo4j+s://123654888.databases.neo4j.io’, database=”neo4j”, csv_dir=”/home/user/”, csv_name=”disease_prepared.csv”) # Create ingestion YAML pyingest_yaml = gen.generate_pyingest_yaml_string() gen.generate_pyingest_yaml_file(file_name=”disease_prepared”) # Load data into Neo4j instance PyIngest(yaml_string=pyingest_yaml, dataframe=disease_df) Querying the Graph Database cypherCopy codeMATCH (n) WHERE n:Demographics OR n:Disease OR n:Symptom OR n:Outcome OR n:HealthIndicator OPTIONAL MATCH (n)-[r]->(m) RETURN n, r, m Visualizing Specific Nodes and Relationships cypherCopy codeMATCH (n:Disease {name: ‘Diabetes’}) WHERE n:Demographics OR n:Disease OR n:Symptom OR n:Outcome OR n:HealthIndicator OPTIONAL MATCH (n)-[r]->(m) RETURN n, r, m MATCH (d:Disease) MATCH (d)-[r:HAS_LAB]->(l) MATCH (d)-[r2:HAS_OUTCOME]->(o) WHERE l.bloodPressure = ‘High’ AND o.result=’Positive’ RETURN d, properties(d) AS disease_properties, r, properties(r) AS relationship_properties, l, properties(l) AS lab_properties Automated Cypher Query Generation with Gemini-1.5-Flash To automatically generate a Cypher query via Langchain (GraphCypherQAChain) and retrieve possible diseases based on a patient’s symptoms and health indicators, the following setup was used: Initialize Vertex AI pythonCopy codeimport warnings import json from langchain_community.graphs import Neo4jGraph with warnings.catch_warnings(): warnings.simplefilter(‘ignore’) NEO4J_USERNAME = “neo4j” NEO4J_DATABASE = ‘neo4j’ NEO4J_URI = ‘neo4j+s://1236547.databases.neo4j.io’ NEO4J_PASSWORD = ‘yourneo4jdatabasepasswordhere’ # Get the Knowledge Graph from the instance and the schema kg = Neo4jGraph( url=NEO4J_URI, username=NEO4J_USERNAME, password=NEO4J_PASSWORD, database=NEO4J_DATABASE ) kg.refresh_schema() print(textwrap.fill(kg.schema, 60)) schema = kg.schema Initialize Vertex AI pythonCopy codefrom langchain.prompts.prompt import PromptTemplate from langchain.chains import GraphCypherQAChain from langchain.llms import VertexAI vertexai.init(project=”your-project”, location=”us-west4″) llm = VertexAI(model=”gemini-1.5-flash”) Create the Prompt Template pythonCopy codeprompt_template = “”” Let’s think step by