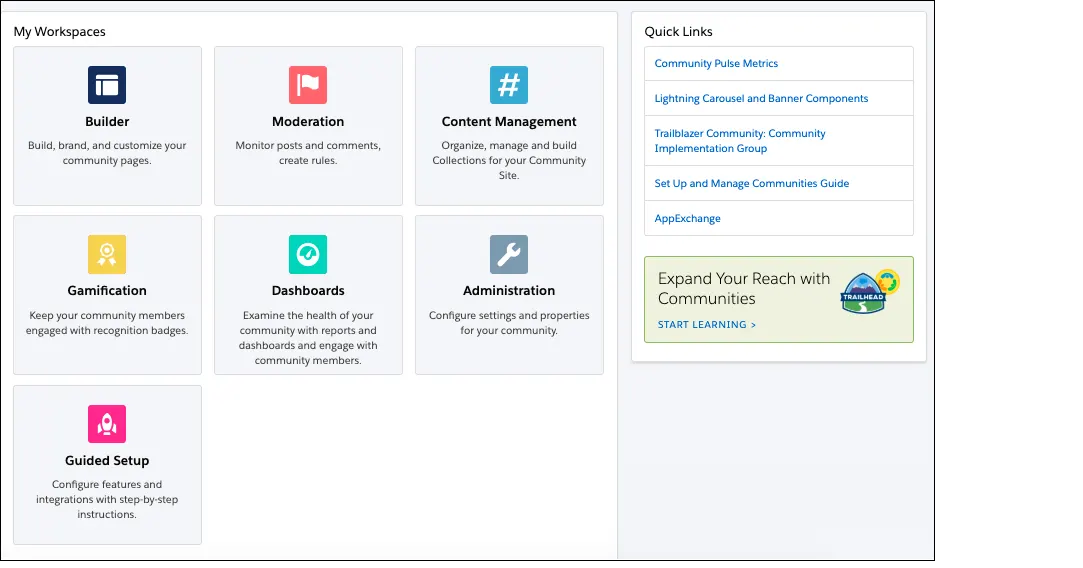
A Salesforce Customer Portal serves as an online support platform for your customers, empowering them to address inquiries independently without needing to contact a customer service representative. Through a Customer Portal, you can personalize and deliver a visually engaging user interface tailored to your customers’ needs.
The primary distinction between a website and a customer portal lies in the audience access. While a website is open to all and attracts traffic from diverse sources, a customer portal is restricted to your customers, prospects, or individuals who create personal accounts with your company.
Also referred to as a client portal, a customer portal is a software interface that provides customers with comprehensive visibility into their interactions with your company. Within the portal, customers can monitor key metrics, track support requests, and easily access reference documents, facilitating seamless collaboration and information sharing.
In Salesforce, both customer portals and communities are built using the Experience Cloud (formerly known as Salesforce Community Cloud), a platform within the Salesforce ecosystem designed for creating CRM-connected websites.
The Salesforce Experience Cloud enables the creation of digital communities tailored for customers, partners, or employees, fostering engagement and interaction with your target audiences.
Key features of Salesforce Experience Cloud include:
- Self-Service Portals for Visitors: Utilize Salesforce Customer Community to develop self-service portals aligned with your business brand. Many organizations integrate knowledge articles and support cases into their portals, managing user access and permissions to ensure relevant content availability.
- Authentication & Security Options: Salesforce portals support single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and security tokens to uphold data privacy and restrict access to authorized users.
- Mobile Responsiveness: Build mobile-responsive portals and communities, enabling users to conveniently access content from any device.
Customer Community Use Cases:
- Offer Self-Service Options: Empower customers with access to digital content like knowledge articles and FAQs, enabling them to resolve issues independently.
- Improve Products & Services: Gather feedback and ideas from customers within the community to drive data-driven decision-making and enhance product/service offerings.
Differences Between Communities and Portals in Salesforce:
Communities Portals
- Utilized by organizations to engage external users (customers, partners, general public)
- Utilized by organizations to share digital content with internal users (employees, contractors)
- External users require community licenses
- Internal users require Salesforce licenses (e.g., Platform, Service Cloud)
- Offers extensive customization options for branding and layout
- Customization options are more limited due to internal user familiarity with the brand
- Includes features like discussion forums, knowledge articles, case management
- Focuses on providing internal users access to reports, dashboards, and company content
Salesforce Experience Cloud incorporates various tools such as Help Center, Authenticated Portal, Customer Community, Einstein Bots, Knowledge, and Experience Builder to enhance self-service capabilities, automate workflows, and deliver personalized support experiences across different channels.