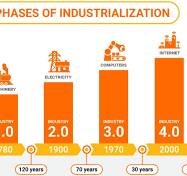
On this Fourt of July, it seems like a good time to discuss the Fifth Industrial Revolution (5IR), also referred to as Industry 5.0, represents a paradigm shift emphasizing collaborative integration between humans and advanced technologies to foster sustainable and human-centric industrial practices. Building upon the digital innovations of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, 5IR aims to merge technological advancements with human ingenuity to develop ethical, inclusive, and environmentally sustainable solutions.
What is the Fifth Industrial Revolution?
Industrial Revolution 5.0: The Transformation of The Modern Manufacturing Process to Enable Man and Machine to Work Hand in Hand.
The fifth IR, also known as Industry 5.0, is characterized by advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and robotics. These technologies are being integrated into manufacturing processes, leading to highly connected and intelligent production systems.
The concept of the Fifth Industrial Revolution, often discussed globally following the Fourth Industrial Revolution, incorporates themes such as sustainability, human-centered approaches, and environmental considerations. Unlike its predecessor, which focused on technological transformations such as AI, IoT, and big data within specific industrial sectors or company units, 5IR seeks broader transformation across industries, companies, and departments. This evolution addresses the limitations of the Fourth Industrial Revolution by integrating global environmental sustainability, human preferences, and circular economy initiatives.
What are the challenges of the fifth IR?
The greatest challenge of the fifth ir is not driven by technology but by humanity. We attach particular concern to the digital technology as it induces a false perception of the reality, and disentangles the human-to-human engagement.
Initiatives of Countries in the Fifth IR
To address the shortcomings of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, various countries are advancing deeper and broader concepts under the banner of the Fifth Industrial Revolution. Initiatives include:
- European Commission’s Industry 5.0: Announced to succeed Industry 4.0, this initiative emphasizes sustainability, human-centeredness, and resilience. It aligns with the European Green Deal policies and aims for carbon-neutral industries and sustainable manufacturing practices.
- Germany’s 2030 Vision for Industrie 4.0: A comprehensive policy framework focusing on autonomy, interoperability, and sustainability. It advocates for collaborative transformation across industries and companies, enhancing labor conditions and resource efficiency.
- Japan’s Society 5.0: Launched as a vision to integrate cyberspace and physical space for economic development and social issue resolution. It emphasizes human-centric solutions and rapid response capabilities during crises.
Key Technologies of the Fifth Industrial Revolution
Central to the Fifth IR are technologies that promote human-machine collaboration and sustainability:
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Designed to work alongside humans without safety barriers, Cobots enhance operational flexibility and safety in various industries including manufacturing, service, healthcare, and retail.
- Smart Cell Industries: Integrating biotechnology and digital technologies to optimize biological cell production. Applications include sustainable materials, biofuels, and advanced medical therapies, facilitated by AI-driven analysis and modularized production processes.
Summary
The 4IR prioritizes interconnected technologies and smart devices that provide value (e.g., the IoT as connections among machines). In the 5IR though, humans and machines (not only machines with one another) metaphorically begin to dance—interacting, engaging, and collaborating regularly
The 5th Industrial Revolution represents a significant advancement over its predecessor by integrating technological prowess with human values and environmental stewardship. It promotes collaborative, sustainable, and resilient industrial practices on a global scale, facilitated by advanced technologies that enhance productivity, quality, and innovation across diverse sectors.
In conclusion, as countries and industries transition towards Industry 5.0, the integration of AI, IoT, robotics, and biotechnology heralds a new era of industrial transformation that not only enhances economic competitiveness but also addresses global challenges through innovative, sustainable solutions.
Industry 6.0(Future Concept), also known as the sixth industrial revolution, is characterized by using advanced technologies such as quantum computing, and nanotechnology over the pre-built Industry 5.0 architecture.
What is the 7th industrial revolution?
Biointelligence and Synthetic Biology: The Seventh Industrial Revolution might witness the convergence of AI and biotechnology, leading to the creation of biologically inspired or synthetic intelligent entities.