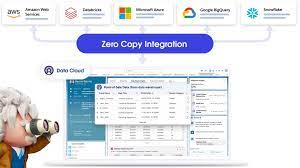
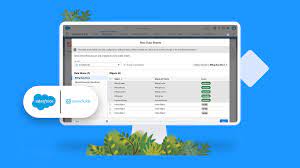
Zero Copy from Salesforce
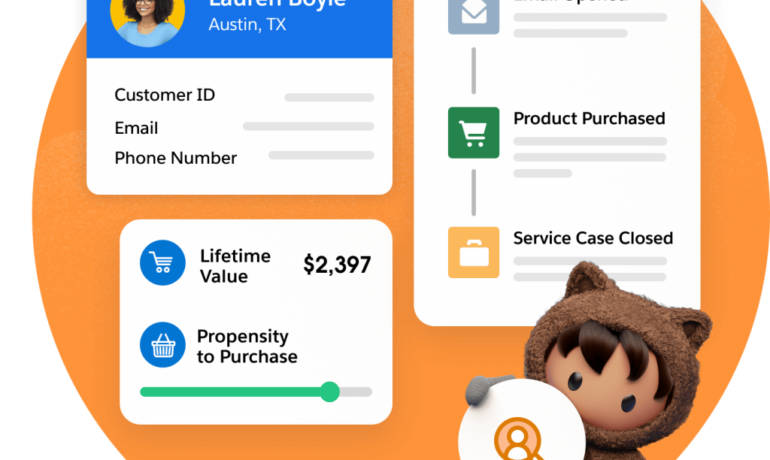
When was the last time you relocated? Remember the hassle of packing up all your stuff, loading it onto a truck, and unpacking everything at your new digs, hoping it all survived the journey? Now, imagine if your furniture and possessions could simply teleport to your new location in perfect condition. While this may not be possible (yet) in the physical world, the concept of zero copy integration offers a similar seamless experience for handling customer data. Zero Copy from Salesforce. Zero copy integration, also known as zero ETL (extract-transform-load), allows data to be shared among multiple data stores without the need for actual movement or duplication. This is particularly advantageous for companies utilizing cloud data warehouses like Snowflake or Google BigQuery. Some companies hesitate to adopt a customer data platform (CDP) due to concerns about duplicating data. However, with zero copy integration, users can leverage the benefits of a CDP—such as data harmonization, identity management, built-in analytics, and activation—without the drawbacks of physical data movement. Some functions related to data have advanced with astonishing speed: generation, dissemination, storage, even security (and yes, that one still has many challenges). But there are others still mired in the stone age—call it the 80s—of the digital era. For example, think copies. How many business professionals still make multiple copies of sensitive data, just as it’s been done for the last four decades? What does this endless duplication do for regulatory risk, security threats and privacy liabilities? This is a symptom of a larger problem: Far from the data-centric universe we all envisioned, we’re beholden instead to the apps used to create, store, and distribute data. There’s an app for everything, but also a database for every app, leading to dozens of data silos undergoing hundreds of integrations, increasing fragmentation, complexity, and costs. The basic idea, according to Dan DeMers, Cinchy’s CEO, is that the framework aims to remove application data silos by using access-based data collaboration versus standard API-base data integration that involves copying data and branding it with complex app-specific coding. This would be done by access controls set in the data layer. It would also involve: What is Zero Copy Integration? Zero copy integration enables access to data stored in multiple databases simultaneously without the need to move, copy, or reformat the data. This approach not only facilitates faster and easier access to data but also reduces costs and minimizes the risk of errors associated with data movement or transformation. Comparing Traditional Methods with Zero Copy Integration: Traditional Methods: Zero Copy Integration: How It Works: From CDP to Data Warehouse In this scenario, data is accessed from the CDP and shared with the data warehouse, a process known as data sharing. The steps typically involve: How It Works: From Data Warehouse to CDP Conversely, in this scenario, data is accessed from the data warehouse and integrated into the CDP, a process referred to as data federation. The steps typically involve: Real-World Application: How Buyers Edge Utilizes Zero Copy Technology Buyers Edge, a leading procurement optimization company in the food service industry, leverages zero copy technology to access purchase data stored in a data warehouse while building a unified customer profile in a CDP. This allows them to provide better customer insights to their sales and marketing teams. By eliminating the need for data movement, duplication, or reformatting, zero copy technology streamlines data access, harmonizes data for insights and analytics, and provides a real-time holistic view of customers. As data volumes continue to grow exponentially, technologies like zero copy integration will play a crucial role in simplifying data management and facilitating seamless access to valuable insights. Whether it’s optimizing business processes or enhancing customer experiences, zero copy integration empowers organizations to navigate the data landscape with agility and efficiency. Be a zero copy hero and unlock the full potential of your data management strategy. “In today’s digital landscape, companies struggle with islands of data spread across various systems. With this global ecosystem of partners, companies can access all of their data, no matter where it resides, and unlock the power of all of that data within Salesforce — creating more personalized customer interactions and establishing a foundation for trusted AI, in less time and at lower cost.” Brian Millham, President and Chief Operating Officer at Salesforce The Zero Copy Partner Network features initial partners Amazon Web Services (AWS), Databricks, Google Cloud, and Snowflake, and adds Microsoft, all committed to zero copy integrations with Salesforce that give customers a secure and cost-effective way to connect and take action on all of their data New zero copy support for data warehouses and data lakehouses built on open table formats, like Apache Iceberg, with Salesforce Data Cloud, removes the need to copy or move data, so customers can unlock their data, powering Customer 360 experiences with AI, automation, and analytics The network includes Salesforce ISV partners, building new Zero Copy Data Kits to bring valuable new datasets to Salesforce Data Cloud, and Salesforce SI partners including Accenture, Cognizant, Deloitte Digital, and PwC, helping customers with zero copy Salesforce Data Cloud implementations. Like Related Posts Salesforce OEM AppExchange Expanding its reach beyond CRM, Salesforce.com has launched a new service called AppExchange OEM Edition, aimed at non-CRM service providers. Read more The Salesforce Story In Marc Benioff’s own words How did salesforce.com grow from a start up in a rented apartment into the world’s Read more Salesforce Jigsaw Salesforce.com, a prominent figure in cloud computing, has finalized a deal to acquire Jigsaw, a wiki-style business contact database, for Read more Service Cloud with AI-Driven Intelligence Salesforce Enhances Service Cloud with AI-Driven Intelligence Engine Data science and analytics are rapidly becoming standard features in enterprise applications, Read more