Top Data Analytics Tools for Chronic Disease Management
Effective management of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and hypertension requires healthcare organizations to leverage powerful data and analytics tools. With 129 million Americans affected by at least one chronic disease—a number that’s growing—the burden on the U.S. healthcare system continues to rise. To address this, stakeholders are adopting data-driven chronic disease management strategies focused on disease monitoring, care coordination, and preventive care.
Healthcare IT advancements, especially electronic health records (EHRs), have made it easier to gather and store data, which, in turn, fuels population health initiatives and improves patient outcomes. The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality highlights that using health IT tools can significantly enhance chronic disease management by promoting efficient care delivery, information-sharing, and patient education. However, selecting and adopting the right analytics tools remains challenging. Here are five essential data analytics tools that healthcare providers can leverage for effective chronic disease management.
1. Population Health Management (PHM) Technologies
Chronic diseases affect entire patient populations and vary across health systems, making a one-size-fits-all approach ineffective. PHM tools consolidate data from various sources, including EHRs, disease registries, social determinants of health (SDOH) data, and claims data, to create a holistic view of patient populations. By integrating these data points, PHM tools identify high-risk populations, streamline care delivery, and reduce health disparities, making them crucial for managing chronic conditions.
Patient engagement tools are also essential within PHM for chronic disease management. They help promote patient access to care, support the use of self-management apps to encourage behavior change, and improve digital health literacy.
2. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics are increasingly valuable as they allow healthcare providers to anticipate disease patterns, track comorbidities, and optimize patient outcomes. In chronic disease management, predictive modeling helps in identifying at-risk patients and in flagging care gaps, enabling healthcare providers to intervene proactively.
These tools are essential for preventive health efforts and can support tasks beyond prevention, including early detection, personalized treatment planning, resource allocation, and operational efficiency. Predictive analytics, often integrated into AI-powered chronic disease management platforms, process large volumes of data quickly, helping healthcare providers tackle complex cases, from risk screening to precision medicine.
3. Risk Stratification
Risk stratification involves categorizing patients based on health status and other factors, helping healthcare providers allocate resources more effectively. This method enables providers to deliver proactive, risk-adjusted care to patients at different stages of chronic disease. Risk stratification also aligns with predictive analytics, allowing for better-informed early detection, diagnosis, and personalized treatment plans.
Incorporating SDOH data into risk prediction models further promotes health equity by addressing care access and discrimination issues that patients with chronic diseases often face. With a focus on equity, risk stratification contributes significantly to value-based care models.
4. Wearables and Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Wearables like smartwatches and other RPM devices allow providers to monitor patients outside clinical settings. Continuous blood glucose monitors, pulse oximeters, and blood pressure monitors, among other sensors, deliver near real-time insights for chronic disease management.
RPM provides a vital data source, helping healthcare providers track patient progress and adjust care plans as needed. This modality has shown success in bridging chronic care gaps, particularly in managing diabetes, hypertension, and cardiac conditions. RPM tools, in combination with other analytics technologies, are particularly valuable for enhancing outcomes in populations with limited access to frequent in-person care.
5. Data Visualization
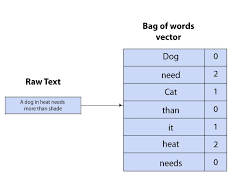
Data visualization translates complex information into visual formats like maps, graphs, and dashboards, making it easier to identify trends and patterns in large datasets. Visualization is essential for healthcare organizations dealing with massive amounts of data, as it enables more intuitive insights and evidence-based decision-making.
Dashboards are particularly useful for displaying insights from EHRs and other data sources. For instance, the Regenstrief Institute has developed public health dashboards for chronic diseases like sickle cell disease. These interactive visualizations help patients, providers, and public health officials understand disease prevalence and guide population health initiatives.
The CDC’s Chronic Disease Indicators (CDI) tool is another powerful visualization resource, offering data on chronic disease trends by race, ethnicity, age, and gender. This tool supports evidence-based decision-making for PHM and fosters health equity.
Building a Foundation for Chronic Disease Management
These five data analytics tools—PHM technologies, predictive analytics, risk stratification, RPM, and data visualization—provide a robust foundation for managing chronic diseases effectively. By integrating these tools, healthcare providers can address care gaps, improve preventive care, and promote health equity across patient populations, creating a more resilient healthcare system capable of tackling the rising burden of chronic diseases.
🔔🔔 Follow us on LinkedIn 🔔🔔