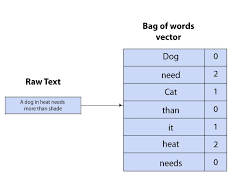
A voice agent, also known as a voice AI agent, is a system that uses artificial intelligence (AI) to understand, interpret, and respond to human speech, enabling natural, conversational interactions for tasks like answering questions, providing information, or completing actions.
Functionality:
Voice agents use technologies like natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to engage in conversations, answer queries, and perform tasks, much like a customer service representative would.
- How it works:
- Speech-to-Text (STT) or Speech Recognition: The user’s speech is converted into text.
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU): The AI analyzes the text to understand the user’s intent.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS): The AI generates an appropriate response and converts it back into speech.
- Applications:
Voice agents are used in various fields, including:- Customer Service: Automating repetitive tasks and providing 24/7 support.
- Home Automation: Controlling devices with voice commands.
- E-commerce: Enabling voice-enabled shopping and payments.
- Healthcare: Improving patient care.
- Automotive: Navigating, entertaining, and communicating in vehicles.
- Benefits:
- Cost Savings: Automating tasks reduces the need for large customer service teams.
- Increased Efficiency: AI voice agents can handle multiple interactions simultaneously.
- Improved Customer Experience: Natural and conversational interactions can enhance customer satisfaction.
- Examples:
- Virtual Assistants: Devices like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri.
- Call Center Automation: AI-powered systems that handle customer inquiries over the phone.
- Voice-Enabled Applications: Apps that allow users to interact with them using voice commands.
Voice AI agents represent a transformative leap in how humans interact with technology. These sophisticated systems combine speech recognition, natural language understanding, and human-like speech synthesis to enable fluid, real-time conversations. Unlike traditional AI tools, voice AI agents can autonomously reason, make decisions, and execute tasks—revolutionizing industries from customer service to healthcare.
What Are Voice AI Agents?
Voice AI agents are autonomous software systems that:
✔ Understand spoken language (speech recognition).
✔ Reason like humans (powered by large language models).
✔ Respond with natural-sounding speech (text-to-speech synthesis).
✔ Perform tasks with minimal human intervention (agentic workflows).
They excel in 24/7 interactive services, such as customer support, personal assistants, and accessibility tools, offering human-like interactions at scale.
How Voice AI Agents Work
Voice AI agents integrate multiple AI disciplines:
1. Speech Recognition (ASR)
- Converts spoken words into text.
- Modern systems use transformer-based models (e.g., Whisper, Deepgram) instead of older statistical models (HMMs).
- Must handle accents, dialects, and background noise.
2. Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
- Powered by LLMs (GPT-4, Gemini, Llama 3).
- Determines user intent and formulates responses.
- Can incorporate Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for real-time data access.
3. Decision-Making & Task Execution
- Agents use planning, tool integration (APIs, databases), and multi-step reasoning.
- Can adapt dynamically (unlike rigid chatbots).
4. Speech Synthesis (TTS)
- Converts text responses into natural-sounding speech.
- Advanced models (e.g., ElevenLabs, Amazon Polly) mimic intonation, emotion, and pacing.
Key Advancements Over Traditional Assistants
| Feature | Virtual Assistants (Siri, Alexa) | Modern Voice AI Agents |
| Reasoning | Limited, scripted responses | Dynamic, LLM-powered decisions |
| Task Complexity | Single-step commands | Multi-step workflows |
| Adaptability | Static knowledge | Learns from interactions |
| Personalization | Basic user profiles | Context-aware responses |
Architecture of a Voice AI Agent
A typical client-server setup includes:
Client-Side
- Input: Microphone (speech), text, or multimodal inputs.
- Output: Speaker (TTS), screen, or API responses.
Server-Side
- ASR Service – Transcribes speech to text.
- LLM Agent – Processes intent, retrieves data, plans actions.
- TTS Service – Converts responses to lifelike speech.
- Memory & Databases – Stores context for personalized interactions.
Communication Protocols:
- WebRTC (real-time browser apps).
- VoIP (telephony integrations).
Challenges & Limitations
Despite rapid progress, voice AI agents still face hurdles:
🔹 Accents & Dialects – Performance drops with underrepresented languages.
🔹 Speech Disorders – Struggles with stuttering or atypical speech patterns.
🔹 Continuous Learning – Requires frequent retraining to stay current.
🔹 Privacy Concerns – Handling sensitive voice data securely.
How to Build a Voice AI Agent
- Choose an ASR Model (Whisper, Deepgram, Nova-2).
- Select an LLM (GPT-4, Gemini, Llama 3 for reasoning).
- Optimize for Agentic Behavior (ReAct, LangChain, fine-tuning).
- Integrate TTS (ElevenLabs, Amazon Polly).
- Deploy (Cloud APIs, on-device with Ollama/Llama.cpp).
Real-World Applications
✅ Customer Service – Automated call centers (Vapi, Skit.ai).
✅ Healthcare – Voice assistants for patients & diagnostics.
✅ Education – Personalized tutoring & language learning.
✅ Accessibility – Assistive tech for visually impaired (Be My AI).
✅ Smart Homes – Voice-controlled IoT devices (Alexa, Google Home).
The Future of Voice AI Agents
As LLMs, speech synthesis, and agentic frameworks improve, voice AI will:
- Handle multilingual, emotionally intelligent conversations.
- Seamlessly integrate with enterprise workflows.
- Become ubiquitous in phones, cars, and wearables.
However, ethical AI development remains critical to address biases, privacy, and security.
Final Thoughts
Voice AI agents are reshaping human-computer interaction, moving beyond rigid chatbots to true conversational partners. Businesses adopting this tech early will gain a competitive edge—while those lagging risk obsolescence.
The era of talking machines is here. Are you ready?