The Resurgence of Vectorized Data in the Age of Generative AI
Advancements in generative AI are driving renewed interest in vector databases, with organizations uncovering new applications for this established yet underutilized technology. Vectors, long integral to AI, are now recognized as foundational for developing sophisticated generative AI applications and transforming enterprise workflows. Resurgence of Vectorized Data.
Why Vectors Are Vital in Generative AI
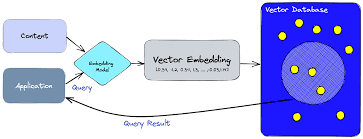
Vectors enable AI to learn and draw insights by identifying similarities within datasets. Unlike traditional indexing, vectors offer advanced capabilities for contextual understanding. For generative AI models, such as OpenAI’s GPT or Google’s Gemini, vectors allow data teams to train AI systems on enterprise data using techniques like retrieval-augmented generation.
By assigning data to vectors, organizations ensure AI models can access contextually similar information from trusted, governed data sources, delivering accurate and informed responses. This makes vectors essential for tasks like personalized recommendations, enhanced search, and more.
What Are Vectors?
In AI, a vector represents data as a series of numerical values arranged in a specific order, akin to coordinates in a multidimensional space. For example:
- A word vector might encode meanings and contexts of words. Words with similar meanings, such as “cat” and “dog,” have similar vector representations.
- Image vectors encapsulate visual information like shapes or patterns.
- User profile vectors may describe preferences, location, and attributes.
These multidimensional representations allow AI to recognize patterns and relationships across vast datasets.
Applications of Vectorized Data
The growing focus on generative AI has unveiled several innovative use cases for vectorized data:
- Semantic Search
Vectorized data powers semantic search by understanding the intent behind queries. This enables search engines to provide more relevant and context-aware results, improving user experiences. - Personalized Recommendations
Recommendation engines use vectors to analyze user profiles, preferences, and content. Industries like e-commerce and streaming can leverage this for tailored experiences that boost engagement and conversions. - Cybersecurity Anomaly Detection
Vectors help monitor network behavior, identifying anomalies that may indicate security breaches or fraud by analyzing deviations from normal patterns. - Content Creation
Vectors are central to generative AI models like GPT and GANs, enabling the creation of realistic text, images, and sounds. Organizations can use this for automated content production. - Improved Customer Service
By vectorizing past support cases, organizations can quickly find similar cases, leading to faster and more informed customer support responses. - Advanced Clustering and Analysis
Vectors allow organizations to analyze large datasets—emails, documents, or social media posts—to identify patterns and insights, aiding in financial modeling, supply chain planning, and more. - Real-Time Language Translation
Vectors facilitate instant translation by maintaining context and meaning, breaking language barriers and enabling global business communication.
Key Considerations for Businesses – Resurgence of Vectorized Data
Organizations embracing vectorized data gain several advantages:
- Scalability: Vectors excel in processing vast datasets, far surpassing traditional indexing methods.
- Precision: Vectors enable nuanced data exploration, improving accuracy in identifying patterns and similarities.
By adopting vectors, businesses can unify and process diverse data types—text, images, or audio—under a common framework.
A Strategic Imperative in the AI Era
Vectorization is not new, but its importance has skyrocketed with generative AI’s rise. Organizations seeking to remain competitive must harness the power of vectors to build smarter systems, gain deeper insights, and strengthen AI-driven processes.
From smarter search engines to AI-powered creative workflows, vectors are the bridge between unstructured data and actionable intelligence. By fully leveraging this technology, businesses can transform their approach to data and secure their place in a rapidly evolving, data-centric world.
🔔🔔 Follow us on LinkedIn 🔔🔔