Understanding Cloud Analytics
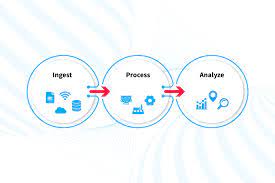
Cloud analytics refers to leveraging cloud computing resources to conduct data analysis more efficiently. It involves using advanced analytical tools to extract insights from vast datasets, presenting information in a user-friendly format accessible via web browsers.
Core Concepts of Cloud Analytics Explained
Cloud analytics shifts traditional data analytics operations, such as processing and storage, to public or private cloud environments. Similar to on-premises analytics, cloud solutions facilitate pattern identification, predictive modeling, and business intelligence (BI) insights. They leverage cloud technologies and algorithms, notably artificial intelligence (AI), including machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL).
Operational Framework of Cloud-Based Analytics
Cloud analytics platforms offer capabilities to build, deploy, scale, and manage data analytics solutions in a cloud-based infrastructure. Examples include cloud enterprise data warehouses, data lakes, and on-demand BI and marketing analytics. Users can subscribe to services under flexible pricing models, alleviating concerns about scalability, performance, and maintenance.
Types of Cloud Analytics
Cloud-based analytics solutions vary by deployment model:
- Public Cloud: Multitenant environments offering scalable resources shared among multiple organizations.
- Private Cloud: Dedicated environments for single organizations, providing enhanced data security and control but with higher costs.
- Hybrid Cloud: Combines public and private clouds, balancing cost efficiency with data governance requirements.
Key Features and Benefits
Cloud analytics offers several advantages:
- Consolidated Data: Integrates disparate data sources into a unified platform for comprehensive insights.
- Scalability: Flexibly scales computing and storage resources based on demand, optimizing cost efficiency.
- Accessibility: Enables self-service access to data for business users, promoting collaboration and real-time decision-making.
- Cost Efficiency: Eliminates upfront hardware costs and reduces maintenance expenses associated with on-premises solutions.
- Security: Implements robust measures for data encryption, compliance, and disaster recovery, enhancing overall data protection.
Applications and Use Cases
Cloud analytics supports diverse applications, including:
- Real-time website traffic analysis and sales forecasting.
- Marketing optimization using social media and customer data analytics.
- Financial services for risk assessment and operational performance monitoring.
- Healthcare and life sciences for genomic data analysis and medical research advancements.
Comparing Cloud Analytics with Traditional Data Analytics
Cloud analytics leverages cloud infrastructure for scalable and flexible data processing, contrasting with traditional analytics tools deployed on-premises. This shift enhances agility and accessibility while reducing operational complexities and costs.
Why Cloud Analytics Matters
Cloud analytics empowers organizations to harness actionable insights efficiently, driving informed decision-making and competitive advantage. It streamlines operations, fosters collaboration, and enhances data reliability and strategic planning capabilities.
Adopting cloud-based analytics enables businesses to transform data into valuable intelligence, fueling innovation and growth. By leveraging cloud-based resources, organizations can achieve operational excellence, secure data-driven insights, and maintain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic business landscape.